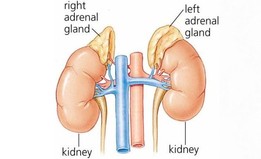
The human adrenal glands are located on top of each of our kidneys. They produce a variety of hormones that bind to our genes and cause them to be activated. There are three types of hormones secreted from the three layers of these adrenal glands. The first layer makes glucocorticoids, steroid hormones that regulate the blood sugar; the next layer makes mineralocorticoids mainly aldosterone, steroids which regulate salt and water balance in the body; the third layer makes sex hormones such as DHEA and testosterone. In the inner core of the adrenal glands is located a tissue known as the medulla, it produces the namesake of the adrenal glands namely adrenalin.
1) Glucocorticoids (Cortisol) – blood sugar regulation
2) Mineralocorticoids (Aldosterone) – salt and water balance
3) Sex hormones – DHEA, testosterone
1) Glucocorticoids (Cortisol) – blood sugar regulation
2) Mineralocorticoids (Aldosterone) – salt and water balance
3) Sex hormones – DHEA, testosterone

When these glands are weak the patient experiences fatigue. This fatigue generally becomes worse as the day wears on and patience with this problem frequently need a nap after lunch. Another prominent symptom is the patient is always thirsty but never seems to retain enough water. This results in low blood pressure and another prominent symptom is thus a condition called “orthostatic hypotension"– the person becomes faint when they get up quickly from a seated position. These patients cannot withstand stress and are easily overwhelmed. They report having difficulty fending off infections. They seem to "catch" every cold that comes around. Besides fatigue the most prominent symptom they report is becoming weak and shaky if they don't eat their meals on a timely basis. This is because their blood sugar falls to levels that their brain cannot operate properly. They forget things. When asked if they have "brain fog", they invariably say "Yes". They report needing a lot of sleep but their sleep doesn't make them feel rested in the morning. They feel like they could sleep another eight hours. Of course because of the biochemical and hormonal derangements they experience they are often depressed and anxious. In fact one reason why they are depressed is that generally they have been to a number of doctors, including endocrinologists, and have been told there is nothing wrong with them and they need antidepressant drugs! This whole story might be familiar to you or to someone you know and care about.
Symptoms of adrenal insufficiency: ·
Symptoms of adrenal insufficiency: ·
- Fatigue – specifically in the afternoon
- Dizziness upon standing
- Poor stress tolerance
- Brain fog
- Anxiety and/or depression
Diet and Hormone Imbalance
Diet is particularly important in these patients. Digestive issues must be addressed, as well as getting their mitochondria to make energy again. But in this special case of a fatigue syndrome it is usually necessary to use low dose, bio-identical hormones to support the body while it heals. The two hormones we use to accomplish this are hydrocortisone (also known as cortisol) and DHEA (dehydroepiandrosterone). These hormones help your body provide energy and give resilience against stress. In addition to this basic approach there are a number of nutritional supplements that can help the patient recover from this dysfunction.
Low dose bio-identical hormones:
Low dose bio-identical hormones:
- Hydrocortisone (cortisol)
- DHEA (dehydroepiandrosterone)
Adrenal Support

Adrenal Advantage – A mixture of adrenal gland extract, licorice, and a number of vitamins known to support adrenal gland chemistry. Dose: One with breakfast and one with lunch. More can be used as desired
ACE Control – A pure and highly concentrated adrenal gland extract. This is used to nourish the adrenal glands back to health and reverse autoimmune attacks against the adrenals (oral tolerance). Dose: 1 to 4 daily.
Pantothenic acid (Vitamin B5) – This vitamin forms the basic structure of Acetyl Coenzyme A, the molecule that carries the fragments of glucose and fat in to the chemical cycles to be burned for energy. Dose: 500 mg. Two or three times daily.
ACE Control – A pure and highly concentrated adrenal gland extract. This is used to nourish the adrenal glands back to health and reverse autoimmune attacks against the adrenals (oral tolerance). Dose: 1 to 4 daily.
Pantothenic acid (Vitamin B5) – This vitamin forms the basic structure of Acetyl Coenzyme A, the molecule that carries the fragments of glucose and fat in to the chemical cycles to be burned for energy. Dose: 500 mg. Two or three times daily.
Blood Sugar Support:
As indicated above, one of the main issues for people with adrenal insufficiency is blood sugar regulation. Specific nutrients to try for this include:
Chromium Picolinate – This mineral is part of the glucose tolerance factor (GTF) which is needed for proper binding of insulin with the insulin receptor on the cell surface. Both diabetics and hypoglycemic patients benefit from this mineral. Dose: 500 µg to two for daily.
Cinnamon – this polyphenol contained within cinnamon tree bark also makes insulin work more effectively. Our colleague Dr. Richard Anderson of the USDA has shown that in addition to its effect on regulating blood sugar, it also breaks up Tau proteins in the brain cells of Alzheimer's patients. The dose has been shown in both animal and human experiments to be 1 g( 1000 µg) three times a day.
Lithium Orotate – there is evidence that this metal helps regulate blood sugar and also encourages growth of new brain cells. As a result it helps people with depression and degenerative brain diseases (Parkinson's disease, dementia, M.S. et al.). We use the small dose of 10 mg twice daily. This dose is small enough that we do not have to check lithium levels as is necessitated with large doses of lithium carbonate used by psychiatrists.
Chromium Picolinate – This mineral is part of the glucose tolerance factor (GTF) which is needed for proper binding of insulin with the insulin receptor on the cell surface. Both diabetics and hypoglycemic patients benefit from this mineral. Dose: 500 µg to two for daily.
Cinnamon – this polyphenol contained within cinnamon tree bark also makes insulin work more effectively. Our colleague Dr. Richard Anderson of the USDA has shown that in addition to its effect on regulating blood sugar, it also breaks up Tau proteins in the brain cells of Alzheimer's patients. The dose has been shown in both animal and human experiments to be 1 g( 1000 µg) three times a day.
Lithium Orotate – there is evidence that this metal helps regulate blood sugar and also encourages growth of new brain cells. As a result it helps people with depression and degenerative brain diseases (Parkinson's disease, dementia, M.S. et al.). We use the small dose of 10 mg twice daily. This dose is small enough that we do not have to check lithium levels as is necessitated with large doses of lithium carbonate used by psychiatrists.
The use of amino acids
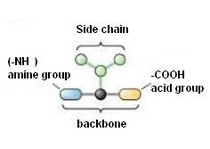
These are the molecules derived from proteins. Our body is constructed of 22 amino acids; eight of them cannot be made in humans (the essential amino acids). Amino acids are used by the body in three ways: they compromise the structure of our body in the form of proteins and enzymes. Secondly, some of them are converted into neurotransmitters. Lastly they can be converted into energy and thus balance blood sugar. They can be used singly or as mixtures.
Glutamine – this amino acid serves as the principal fuel source of the cells that line are intestinal tract and can also be easily converted into glucose to maintain blood sugar and energy. It can also be converted into the
neurotransmitter GABA which calms the central nervous system. Glutamine may be used as capsules or powder at the dose of 1000 to 3000 mg three times daily.
Glycine – works in a similar way to glutamine and is itself a relaxant neurotransmitter in the brain. The dose is 500 to 1000 mg three times daily between meals.
Branched-chain amino acids (BCAA) – these are essential amino acids which are structural building blocks of all tissues. They are also sources of energy when blood sugar falls.
Balanced amino acids – these can be used as an extra source of fully utilizable protein precursors for rebuilding the glands etc. as well as an energy source.
Taurine- Another neurotransmitter in its own right and is very good to stop anxiety. It is a sulfur amino acid and thus will help in detoxification, allergies and inflammation. It is an extremely versatile supplement. Dose 1000 mg three or four times per day. It is non-toxic so you can adjust the dose upward as needed.
Theanine- An amino acid found in green tea. It is a great help for anxiety and sleep problems.
Glutamine – this amino acid serves as the principal fuel source of the cells that line are intestinal tract and can also be easily converted into glucose to maintain blood sugar and energy. It can also be converted into the
neurotransmitter GABA which calms the central nervous system. Glutamine may be used as capsules or powder at the dose of 1000 to 3000 mg three times daily.
Glycine – works in a similar way to glutamine and is itself a relaxant neurotransmitter in the brain. The dose is 500 to 1000 mg three times daily between meals.
Branched-chain amino acids (BCAA) – these are essential amino acids which are structural building blocks of all tissues. They are also sources of energy when blood sugar falls.
Balanced amino acids – these can be used as an extra source of fully utilizable protein precursors for rebuilding the glands etc. as well as an energy source.
Taurine- Another neurotransmitter in its own right and is very good to stop anxiety. It is a sulfur amino acid and thus will help in detoxification, allergies and inflammation. It is an extremely versatile supplement. Dose 1000 mg three or four times per day. It is non-toxic so you can adjust the dose upward as needed.
Theanine- An amino acid found in green tea. It is a great help for anxiety and sleep problems.

